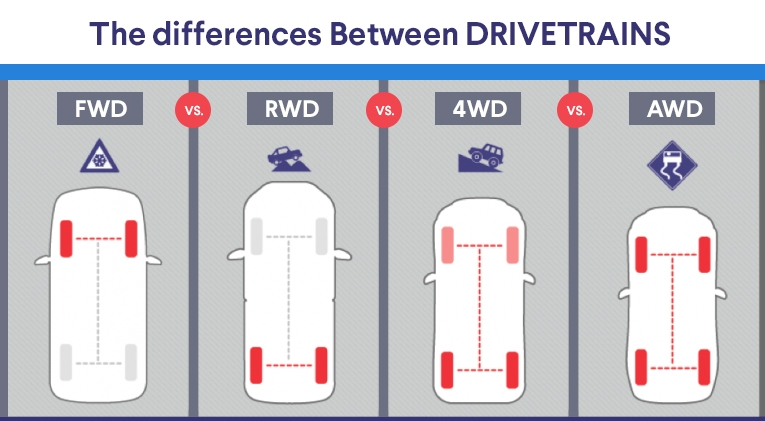

When it comes to choosing a car, one of the most important decisions you’ll have to make is which type of drivetrain to go for. There are four main types of drivetrains available: all-wheel drive (AWD), front-wheel drive (FWD), four-wheel drive (4WD), and rear-wheel drive (RWD). Each has its own strengths and weaknesses, and which one is best for you will depend on your individual needs and preferences. In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at the differences between each type of drivetrain to help you make an informed decision!
All-Wheel Drive (AWD)
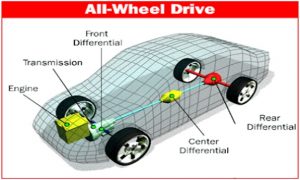
Many drivers confuse AWD vehicles, with 4WD vehicles. Though both systems are designed to engage all four wheels of a vehicle, there are some basic differences between them. All-wheel drive is a drivetrain that uses a combination of front, rear, and center differentials to provide power to all four wheels simultaneously. This system is designed to offer superior traction and handling in a variety of road conditions, including wet or slippery surfaces, and is often found in SUVs, crossovers, and high-performance sports cars. AWD systems typically employ one axle at a time. When the vehicle experiences a loss of traction in one shaft, it automatically sends more power to the other axle to stabilize.
The benefits of AWD include better traction, stability, and handling in poor weather conditions, as well as improved acceleration and cornering performance. However, it can be more expensive to buy and maintain than other drivetrain types.
Front-Wheel Drive (FWD)
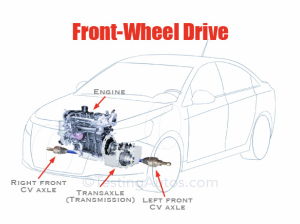
Front-Wheel Drive is found in most cars on the road these days. FWD is a drivetrain that uses the front wheels to provide power and steering to the vehicle. This system is commonly found in compact and mid-size cars.
The benefits of FWD include better fuel economy, a lighter weight, and improved interior space compared to RWD or AWD cars. However, FWD vehicles can be less stable and have less traction in slippery road conditions as well as climbing hills, and may not perform as well in high-performance driving situations.
Four-Wheel Drive (4WD)
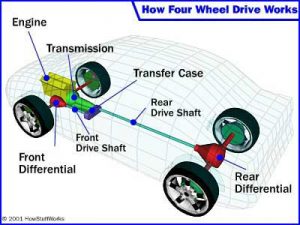
Four-wheel drive is a drivetrain that uses a transfer case to distribute power to both the front and rear wheels simultaneously. This system is designed for off-road use and is commonly found in SUVs, trucks, and other rugged vehicles. Some 4WD vehicles offer two gear ranges of high and low. The reduced range is helpful for scaling steep terrain at low speeds. Modern 4WD additionally provides three toggle options to choose from:
- Full-time systems
- Automated systems (can switch between 2WD and 4WD)
- Part-time systems (requires the driver to switch between 2WD and 4WD, manually)
The benefits of 4WD include superior traction and handling in off-road and low-traction conditions, as well as improved towing and hauling capabilities.
Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD)
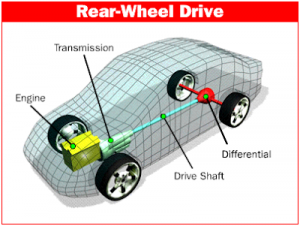
Rear-wheel drive is a drivetrain that uses the rear wheels to provide power for the vehicle. This system is commonly found in sports cars, luxury vehicles, and large trucks, and is often preferred for its balance and handling capabilities.
The benefits of RWD include improved handling, balance, and weight distribution, as well as better acceleration and cornering performance compared to FWD vehicles. However, RWD cars may have less traction in slippery road conditions and may not perform as well in off-road or towing situations.
The choice of the drivetrain will depend on the type of driving you do, your budget, and your personal preferences. If you live in an area with harsh weather conditions or frequently drive off-road, AWD or 4WD may be the best choice. If you want a car with better fuel efficiency and handling in normal driving conditions, FWD may be the way to go. If you’re looking for a car with better handling and balance, RWD may be the ideal choice. Ultimately, it’s important to consider all of the factors and choose the drivetrain that best meets your needs!
Images:
